The human mind is complex. With the help of neuroscientists, modern psychology is still trying to understand how the mind and consciousness work. But we don’t seem any closer to understanding than Sigmund Freud or Carl G. Jung.
Jung’s theories have been widely dismissed as pseudo-philosophy because of their mystical nature. He agreed with ancient wisdom that said there was only one true self. Until we find out this truth, we have a split personality disorder.
Like a puzzle, we have to piece together the mind and discover the Self. Ancient sages knew about this thousands of years ago and expressed archetypal knowledge using symbols in myths.
Jung was innovative and a bit of a sniper. He was inspired by archetypes of ancient cultures used in mythology. Furthermore, he was convinced that archetypes and symbols were part of our genetic memory and recalled by what he called “the collective unconscious”.
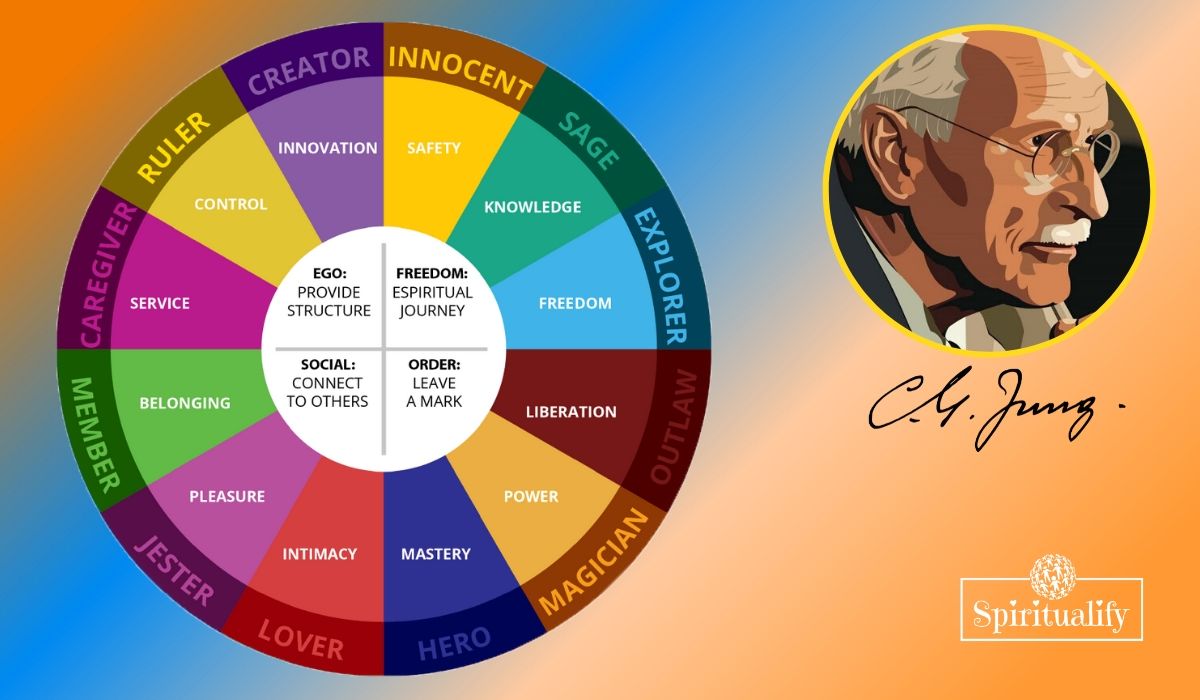
Jung used the concept of archetypes to formulate his own categories of archetypes commonly found in the context of human personality. Most people will recognize three or four dominant personality traits, but we have traces of all 12 that Jung proposes.
Having studied ancient symbolism for several years now, I find it interesting that Jung decided that there are 12 personality types in the same character. The number 12 appears regularly in the ancient symbolism which one finds in the cultures of the whole world:
Jesus had 12 disciples, there are 12 knights of the round table, 12 zodiac/chinses calendar signs, 12 gods in the Greek Pantheon, there were 12 tribes of Jerusalem, the 12 Adityas in Hindu, 12 legitimate successors of Prophet Muhammad, 12 Devas of Japanese Buddhism. And the 12 signs of the zodiac also identify our most dominant character traits.
They are further divided into three groups of four which represent the ego, the soul, and the self (or super soul/ego). Most people can identify at least eight or nine of these archetypes within them, although one is the most dominant, and two others are strong. Which archetypes do you most associate with?
Table of Contents
The Ego Archetypes:
The ego is the center of the consciousness field. Psychoanalysts consider that it is the command HQ that organizes thoughts, feelings, senses, and intuition.
It is the responsibility of the ego to make decisions based on the information it receives from the unconscious mind and the environment around us. When the personalities are unbalanced, it can affect our decision making because we have too many options among the archetypes who want to dominate.
Jung’s ego archetypes are:
The Great Mother:
The Great Mother is also known as the caregiver because of her desire to love, protect, and nourish. She is represented by the Mother Goddess in mythology like Gaia, Rhea, and Parvati. Filled with compassion and generosity, you usually sacrifice your own desires for the benefit of others. The Great Mother is a positive personality trait, but you must also be careful not to suppress or neglect your own emotional needs as they manifest in the form of negative emotions.
Life lesson: Treat others the way you want to be treated, give generously and you will receive in abundance.
The Animus:
Animus is the masculine trait in women. There is a desire to be free and identified as an individual in order to find happiness in oneself. Modern psychology compares Jung’s animus to the orphan in search of themselves without parents to guide them.
When the animus is balanced in women, you are assertive, courageous, decisive, and focused. If the masculine features are unbalanced, you are aggressive, argumentative, and go through the motions of daily life mechanically, and thus detached from reality.
Life lesson: Get in touch with your masculine side.
The Child:
The child is called the innocent archetype of modern psychology. This archetype is someone who has lost touch with his inner self because he is too desperate to adapt to everyone. Because you are loyal and a hopeless romantic, you are loved by almost everyone.
You also have the opportunity to blend in without standing out from the crowd. You want someone’s attention and don’t care who. You just want to be loved even if thinking that way makes you naive. By trying so hard to connect with others, you are doing so at the expense of connecting with yourself and doing what you love and need in life.
Recommended: The 9 Personality Types that are Here to Change the World
The Hero:
The hero is eager to show courage to prove his masculinity and his value to the herd. While you may be seen as overconfident and at times arrogant, you have a strong will and determination to master the skills. You want to be the best at everything, but this streak of competition can also make you look optimistic. The negative aspect of the hero is that he always looks for faults in others to feel good about himself or to choose fights.
Life lesson: Accept yourself and others as individuals.
The Soul Archetypes:
Jung’s attempts to explain the unconscious are demonstrated in his soul archetypes. Here, Jung makes you think about a deeper part of your personality that many people have a glimpse of, but don’t think about it.
Other readers will find that the archetypes of the soul are a dominant character trait.
The Anima:
Also known as the “explorer”, the anima explains the feminine qualities of men. You have a desire to find yourself in something through exploration so don’t be afraid to try new things or new places. The creative feminine quality in you is looking for an authentic and fulfilling experience.
You get bored easily. When the feminine qualities are awakened in men, you have the desire to touch, see, smell, hear, and feel. When the anima is balanced, a man is in touch with his emotions and tender towards others, compassionate and intuitive. When you are out of balance, you are stubborn, moody, and more likely to experience a series of turbulent relationships.
Life lesson: Get in touch with your feminine side.
The Devil:
In ancient symbolism, the devil or demons represent the subconscious nature that Sigmund Freud called the id. Jung called this aspect of our nature the Shadow Self. It is the desire of the inner voice to revolt against the rules of authority in a dysfunctional system.
In the search for peace, harmony, and change, you encounter troubles and disturbances. Your unconventional opinions bother people. Just as Lucifer was cast out of Heaven for challenging God, the devil is trying to regain power by tempting the ego with desires that appeal to your animal instinct.
Life lesson: Summon the courage to make sacrifices.
Recommended: 10 Signs that You Have the Odd and Beautiful Lone Wolf Personality
The Maiden:
The maiden is also known as the lover. You want privacy and are afraid of being alone, unloved, or rejected. Your strategy to be desired by others is to make yourself attractive in one way or another, whether physically, financially, or by bragging.
But your intention to elicit love from others means that you are neglecting the self-love that you need in order to be emotionally stable. To offset the inferiority of this character trait, the maiden is blessed with gratitude, appreciation, and passion.
Life lesson: Love yourself.
The God:
In all ancient cultures and religions, God is the creator. The redeeming personality trait of this aspect of your character is that anything you imagine can be created.
It’s the side of your character that gives you the impetus to realize your vision. Very imaginative and competent, you are endowed with artistic qualities, but you can fall down if you aim for perfection or if you lack patience and search for quick solutions. Your biggest fear is failure.
Life lesson: Understand you are your own God.
The Self Archetypes:
The self is your higher consciousness, the aspect of your true nature that Freud called the Superego. It is the voice that stands to reason if only we can control the survival instincts and the emotions of the id.
The Father:
The father is known as the sovereign in modern psychology and symbolized in mythology by Father Sky. In Greek mythology, the father is personified through the character of Uranus, then Cronos who dethroned his father and took over the Kingdom.
The Kingdom is you. When balanced, the ruler shows an ability to lead and transmits wisdom to others. Your most serious fear is being knocked down or when good things come to an end. If you are out of balance, you suffer when things come to an end and find it difficult to adapt to new lifestyles. You can also be paranoid and misleading.
Life lesson: Don’t try to control others.
Recommended: 14 Signs You Fit in the World’s Kindest Personality Type, ISTJ
The Sage:
The Sage is best known for his ability to think deeply and philosophize about life. You seek the truth and want to understand everything on a deeper level. However, your weakness may be that you think too much and don’t act enough.
The wise sages of the ancient past understood the need for balance and although endowed with wisdom, intelligence and the ability to analyze the world around them, the “wise old man” eventually realized that keeping the mind still and following the flow of life is the only way to find freedom.
Life lesson: Go with the flow.
The Magician:
Jung called the Magician the wise old woman because these qualities complement the wise old man of the Sage. The magician is interested in universal laws and wants to know how to channel their energy to increase their innate powers so that their desires are manifested.
You have the ability to define the plans for your vision, but fear that you will not achieve your goals. To balance this trait, adopt the knowledge of the sage and realize that when you authorize the universal laws unimpeded, they will work the magic that you grant them.
Life lesson: Understand how the Universal laws work.
The Jester:
The jester is the adventurous side of your personality that goes in search of pleasure and leads you to moments of joy. You have a jovial character and want to play games, make jokes, and entertain your company.
Your only weakness is that you often waste time playing instead of focusing on your goals.
Life lesson: Know when to have fun and when to focus.
Jung believed that by embracing the conflicts of your inner personality rather than trying to remove them creates harmony and balance. It is only by allowing unconscious feelings and thoughts to surface, that you discover your True Self, a process that Jung calls individuation.
Recommended Book to Read:
Enneagram Elevation
 Discover How to Use the Enneagram to Uplift You Spiritually
Discover How to Use the Enneagram to Uplift You Spiritually